As daylight hours shorten during fall and winter months, millions of people experience the debilitating effects of seasonal affective disorder. This condition, characterized by persistent sadness, fatigue, and social withdrawal, affects approximately 5% of adults in the United States. Fortunately, light therapy for seasonal depression has emerged as a highly effective, first-line treatment that offers hope for those struggling with winter depression.

This comprehensive guide examines the science behind bright light therapy, provides detailed usage instructions, and explores the extensive research supporting its effectiveness. Whether you’re considering starting light therapy for yourself or seeking to understand treatment options for a loved one, you’ll discover evidence-based insights into this remarkable therapeutic approach.
What is Light Therapy for Seasonal Depression?
Light therapy is a first-line treatment for seasonal affective disorder SAD that involves sitting near a special light box for 30 minutes each morning. This treatment uses bright artificial light at 10,000 lux to compensate for reduced sunlight exposure during the fall and winter months, effectively helping restore disrupted circadian rhythms and brain chemistry that cause seasonal depression symptoms such as persistent sadness, fatigue, and oversleeping.
The treatment represents a significant advancement in treating seasonal depression, offering patients an alternative to antidepressant medication. Unlike selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which can cause weight gain and other side effects, light therapy provides few side effects while delivering comparable therapeutic benefits. This effective treatment can produce remarkable improvements in depression symptoms within just several weeks of consistent use.
A mental health professional typically recommends light therapy as the primary intervention for seasonal affective disorder because it directly addresses the underlying cause of the condition. The therapy involves sitting with eyes open near a light therapy box that emits bright light at specific intensities designed to mimic natural sunlight. This exposure helps regulate the brain’s internal clock, which can become disrupted during winter months when natural light is significantly reduced.
Understanding Seasonal Depression and Light Exposure
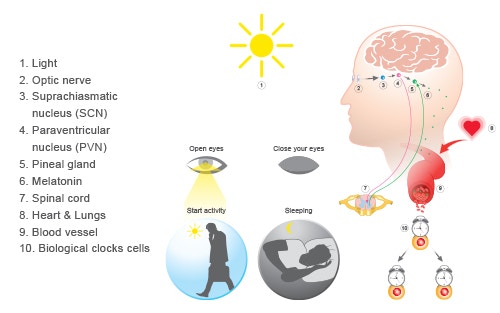
Seasonal affective disorder affects the brain’s circadian rhythm, located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which regulates sleep, hormones, and mood. This critical brain region serves as the body’s master clock, coordinating various biological processes, including the production of neurotransmitters essential for mental health. When winter arrives, and natural sunlight becomes scarce, this internal timing system becomes severely disrupted, leading to the characteristic symptoms of seasonal depression.
The reduced winter daylight disrupts serotonin production and increases melatonin secretion, leading to depressive symptoms that distinguish seasonal affective disorder from major depressive disorder. Light receptors in the retina send signals to brain regions that control mood and cognition, particularly the prefrontal cortex. These neural pathways play a crucial role in maintaining emotional stability and cognitive function throughout the changing seasons.
Winter depression symptoms include hypersomnia, hyperphagia, weight gain, and social withdrawal, creating a distinct pattern different from typical depression. Unlike major depression, which may occur year-round, seasonal depression follows a predictable seasonal pattern, typically beginning in the fall and continuing through the winter months. This cyclical nature provides valuable clues about the underlying biological mechanisms and explains why light exposure therapy proves so effective for this particular mood disorder.
The connection between light exposure and mood regulation involves complex neurochemical processes that researchers continue to study. Environmental therapeutics specialists have identified that even on a cloudy day, outdoor light, which provides approximately 1,000 to 10,000 lux, can significantly impact brain chemistry. This understanding has revolutionized the treatment of SAD and highlighted the importance of maintaining adequate light exposure throughout the winter months.
How Light Therapy Works
Bright light exposure advances delayed circadian rhythms by signaling the suprachiasmatic nucleus through melanopsin-containing retinal cells. These specialized photoreceptors are distinct from the rods and cones responsible for vision and instead serve as the primary pathway for circadian rhythm regulation. When exposed to bright light, particularly during the first hour after waking, these cells send powerful signals to the brain’s master clock, helping to reset and maintain proper timing of various biological processes.
The therapy reduces serotonin transporter binding activity, thereby increasing synaptic serotonin availability and improving mood. This mechanism explains why light therapy can help individuals with both seasonal and nonseasonal depression. Research has shown that serotonin, often called the “happiness neurotransmitter,” plays a crucial role in mood regulation, and light exposure directly influences its availability in the brain. This antidepressant effect occurs through natural biological processes rather than pharmaceutical intervention.
Light therapy also suppresses excess melatonin production during daylight hours, helping normalize sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin, the hormone responsible for promoting sleepiness, typically rises in the evening and falls in the morning. However, during winter months, this natural rhythm becomes disrupted, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness and disrupted nighttime sleep. Bright light exposure in the morning helps restore this crucial hormonal balance.
Blue wavelength light around 480 nanometers proves most effective for circadian rhythm entrainment, though full-spectrum white light remains the standard for sad treatment. This specific wavelength most effectively stimulates the melanopsin-containing retinal cells responsible for circadian regulation. However, light therapy boxes typically use broad-spectrum white light to ensure safety and effectiveness across different individual responses. The systematic review of clinical evidence consistently demonstrates that properly administered light therapy works through these multiple complementary pathways to restore normal brain function.
Proper Light Therapy Usage Guidelines
Using a light therapy box requires specific protocols to maximize effectiveness and safety. The standard recommendation is to use a 10,000 lux light box for 30 minutes every morning, ideally within the first hour after waking. This timing proves crucial because morning light exposure most effectively signals the brain to reduce melatonin production and increase serotonin availability, creating the optimal conditions for mood improvement.
Position the light box 16-24 inches away, either directly in front or slightly to one side of your visual field. The device should be angled downward toward your eyes, mimicking the sun’s natural position. Keep eyes open but avoid staring directly at the light source; you can read, eat breakfast, or work during treatment. This positioning ensures adequate light intensity reaches the retinal cells responsible for circadian regulation while maintaining safety and comfort.

Begin treatment in early fall, ideally September or October, before symptoms worsen, and continue through winter until spring. This proactive approach, recommended by most mental health professionals, helps prevent the full development of seasonal depression symptoms. Starting light therapy before the onset of severe symptoms proves more effective than waiting until depression symptoms become debilitating.
Choose light boxes certified by organizations like the Center for Environmental Therapeutics that filter harmful UV rays. Quality devices should produce minimal ultraviolet light to ensure safety during prolonged use. Smaller light boxes may seem convenient, but they often fail to provide adequate light intensity across the full visual field. When selecting equipment, prioritize devices with large enough surface areas to deliver consistent 10,000 lux exposure.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
Consult a healthcare provider before starting, especially if you have conditions such as bipolar disorder, as light therapy may trigger manic episodes in susceptible individuals. This condition requires careful monitoring because the same mechanisms that improve depression symptoms can potentially destabilize mood in people with bipolar disorder. A mental health professional can help determine whether light therapy represents a safe treatment option or if alternative approaches would be more appropriate.
People taking medications that increase light sensitivity, such as certain antibiotics and anti-inflammatories, should seek medical guidance before starting light therapy. These photosensitizing medications can increase the risk of eye damage or skin irritation when combined with bright light exposure. Additionally, individuals taking medication for other conditions should discuss potential interactions with their healthcare provider.
Those with retinal conditions, glaucoma, or cataracts need an ophthalmologist’s approval before treatment. These eye conditions can affect how light is processed, potentially increasing the risk of eye damage from exposure to bright light. An eye care professional can assess individual risk factors and provide guidance on safe usage protocols.
Pregnant women and elderly individuals often benefit from light therapy, as it avoids medication side effects associated with antidepressant medication. The treatment’s safety profile makes it particularly attractive for populations where pharmaceutical interventions carry additional risks. However, even these generally safe populations should consult with healthcare providers to ensure proper monitoring and usage.
Effectiveness and Research Evidence
The light therapy antidepressant effect typically appears within 3-7 days, significantly faster than traditional antidepressants, which require several weeks to show benefits. This rapid response time represents a major advantage for individuals suffering from seasonal depression, allowing them to experience relief much sooner than with pharmaceutical alternatives. Clinical trials consistently show that when light therapy is effective, most people notice symptom improvement within about 1 week of starting treatment.
Combining light therapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors improves response rates in patients according to research from associate professors at Harvard Medical School. This combination approach allows individuals to potentially use lower doses of antidepressant medication while achieving superior therapeutic outcomes. The research demonstrates that light therapy can serve as either a standalone treatment or as an effective adjunct to existing depression treatments.
Research reveals that morning light exposure is significantly more effective than evening light exposure. This finding aligns with chronobiological principles, which hold that morning light has a greater influence on circadian phase adjustment. The evidence consistently supports morning administration as the optimal timing for light therapy sessions.
Side Effects and Tolerability
Common mild side effects include eye strain, headaches, and initial irritability that typically resolve within a week of consistent use. These temporary effects usually diminish as individuals adapt to the treatment regimen. Most users find these minor inconveniences manageable, especially when weighed against the significant improvement in depression symptoms and overall quality of life.
Less frequent effects may include nausea, agitation, or sleep disturbances if treatment occurs too late in the day. The timing of light exposure proves crucial not only for effectiveness but also for minimizing potential side effects. Using the light box too close to bedtime can interfere with natural melatonin production and disrupt sleep patterns, potentially exacerbating rather than improving mood symptoms.
The side effect profile proves much more favorable than antidepressant medication, which can cause weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and withdrawal symptoms. Unlike pharmaceutical interventions, light therapy doesn’t require gradual dose adjustments or complex withdrawal protocols. This safety advantage makes light therapy particularly attractive for individuals concerned about medication side effects or those seeking non-pharmacological treatment approaches.
Most users can safely continue light therapy throughout winter with minimal adverse effects. The nonprofit organization guidelines emphasize that properly administered treatment carries low risk when used according to established protocols. Long-term use studies show that individuals can safely use light therapy seasonally for many years without developing tolerance or experiencing significant adverse effects.
Research indicates that light therapy produces few side effects compared to other treatment options for mood disorders. The natural mechanism of action, which works by restoring normal biological processes rather than introducing foreign substances, contributes to this favorable safety profile.
Light Therapy Equipment and Costs

Clinically tested light boxes cost approximately $150-$300, and some insurance companies cover devices for diagnosed cases of SAD. These therapeutic devices represent a one-time investment that can provide years of effective treatment. When compared to the ongoing costs of antidepressant medication or regular therapy sessions, light boxes often prove more economical over time.
Key specifications include 10,000 lux output, UV filtering, and a large enough light surface area of at least 12 by 15 inches. The light intensity measurement proves critical because insufficient lux levels won’t provide therapeutic benefits. Quality devices should clearly display their lux output at specific distances to help users position the device correctly for optimal treatment.
Dawn-simulation alarm clocks provide gradual morning light increases but are less effective than standard light therapy boxes. While these devices can supplement treatment, they typically don’t provide sufficient light intensity to treat depression symptoms effectively. Most dawn simulators produce only a few hundred lux, far below the 10,000 lux threshold required for therapeutic effect.
Avoid inexpensive imitations that may not meet therapeutic light intensity requirements or safety standards. Many consumer products marketed as “light therapy” devices fail to provide adequate lux levels or proper UV filtering. When selecting equipment, prioritize devices specifically designed for treating sad and certified by reputable organizations specializing in environmental therapeutics.
Consider features such as adjustable positioning, timer controls, and portability when selecting a device. Some smaller light boxes offer convenience for travel but may require longer treatment sessions to achieve the same therapeutic effect. The most effective treatment approach involves finding a balance between device effectiveness and practical usability that encourages consistent daily use.
Natural Light Alternatives
Early morning outdoor walks provide natural light therapy, with bright sunny days delivering approximately 50,000 lux of natural sunlight. This intensity far exceeds the 10,000 lux provided by artificial light boxes, making outdoor exposure highly effective when weather conditions permit. Even brief exposure to natural outdoor light can provide significant therapeutic benefits for individuals with seasonal depression.
Even on a cloudy day, outdoor conditions offer approximately 10,000 lux, equivalent to therapeutic light box intensity. This fact surprises many people who assume that overcast conditions provide insufficient light for therapeutic benefit. Walking outdoors for 30 minutes shortly after sunrise can provide benefits similar to those of artificial light therapy, even during winter months when cloud cover is common.
Walking for 30 minutes shortly after sunrise can provide benefits similar to those of artificial light therapy, while adding the additional advantages of physical exercise. This combination approach addresses multiple aspects of seasonal depression, including the mood benefits of physical activity and the circadian rhythm regulation provided by light exposure. The exercise component may enhance the overall antidepressant effect beyond what light exposure alone provides.

Sunglasses can be worn on bright days without reducing therapeutic benefits, as adequate light still reaches the retinal cells responsible for circadian regulation. This flexibility allows individuals to protect their eyes from glare while still receiving therapeutic light exposure. However, very dark sunglasses may reduce the therapeutic effect, so lighter tints are preferable when possible.
For those with mobility limitations, sitting by a large south-facing window for 15 minutes can provide modest mood benefits during sunny periods. While this approach provides less intensive light exposure than dedicated light therapy devices, it represents an accessible option for individuals unable to use traditional equipment or go outdoors. The combination of natural sunlight and a comfortable indoor environment can make this approach particularly appealing for elderly individuals or those with physical limitations.
Even indirect natural sunlight exposure through windows provides some therapeutic value, though glass filtering reduces the overall light intensity. Strategic positioning near large windows during morning hours can supplement other treatment approaches and help maintain circadian rhythm regulation throughout the winter months.
Light Therapy Conclusion
Light therapy for seasonal depression represents a scientifically validated, accessible treatment that can significantly improve the quality of life for millions affected by seasonal affective disorder. With significant response rates and a rapid onset of benefits within one week, this effective treatment offers hope for those struggling with winter depression. The therapy’s favorable safety profile, minimal side effects, and proven effectiveness make it an excellent first-line treatment option.
The extensive research evidence confirms that bright light therapy works through well-understood biological mechanisms. By restoring proper circadian rhythms and normalizing neurotransmitter function, this treatment addresses the root causes of seasonal depression rather than merely masking symptoms.
Whether using a dedicated light therapy box or incorporating natural light exposure through outdoor activities, individuals have multiple options for implementing this evidence-based approach. The key to success lies in consistent use, proper timing, and following established protocols for safety and effectiveness.
If you’re considering light therapy for seasonal depression, consult with a mental health professional to determine the best approach for your individual situation. With proper guidance and consistent use, light therapy can help you reclaim your winter months and maintain optimal mental health throughout the seasonal changes.
(706) 521-5290
To view the original version on Foot Palace, visit: https://yourfootpalace.com/light-therapy-for-seasonal-depression/